
What Does GDDR and DDR Stand For?
DDR stands for Double Data Rate, and GDDR stands for Graphics Double Data Rate. However, DDR and GDDR are completely different technologies—they don't share the same standards for speed, bandwidth, or other specifications. DDR is developed for CPUs (and CISC architectures), while GDDR is designed for graphics (and RISC architectures).
The full name GDDR7 SDRAM stands for Graphics Double Data Rate Type 7, Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory. Both DDR and GDDR use SDRAM—the foundation of memory used in desktops (UDIMM DDR5), in laptops (SODIMM DDR5), low-power devices (LPDDR5), and graphics processing units (GDDR6, GDDR6X, and GDDR7 in both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs).
Recent developments have introduced unified memory, a software abstraction that allows both CPU and GPU to share a memory pool. Popularized by Apple Macs, AMD APUs, and NVIDIA Grace, unified memory can use DDR or HBM memory. Unified memory is now used in the popular NVIDIA DGX Spark.
DDR: Low-Latency System Memory for General-Purpose Computing
DDR (Double Data Rate) memory is the primary system RAM used by CPUs. Unlike GDDR (optimized for bandwidth), DDR is designed for low latency, ensuring the CPU can access data and instructions as quickly and responsively as possible. This makes DDR ideal for running applications, managing the operating system, handling interrupts, and coordinating GPU workloads.
While CPU memory doesn’t reach the extreme transfer rates of GDDR or HBM, its strength lies in its ability to respond rapidly to a wide variety of small, random access patterns typical of general-purpose computing.
- Access times are optimized, measured in clock cycles (CAS Latency).
- Frequencies: DDR5 ranges from 4800 MT/s to beyond 8400 MT/s.
- Responsiveness over raw bandwidth: matches how CPUs process diverse, branching instruction sets.
These design choices ensure the CPU is never waiting long for data it needs to execute instructions, manage threads, or coordinate system resources.
Why DDR Matters
DDR provides several key benefits that directly affect everyday computing and workstation performance:
- Low Latency for CPU Operations: Essential for running applications, executing instructions, and managing real-time system tasks.
- High Efficiency for Random Access Patterns: Supports the CPU’s need to retrieve small chunks of data rapidly.
- Scalable Frequencies with Each Generation: DDR5 delivers higher transfer rates while improving efficiency and capacity.
- Latency vs. Frequency Balance: While DDR5 may have higher CAS Latency numbers than DDR4, its increased frequency results in similar or better absolute latency.
| DDR Generation | CAS Latency | Frequency | Absolute Latency |
| DDR4 | CL16 | 3200 MT/s | 10ns |
| DDR4 | CL18 | 3600 MT/s | 10ns |
| DDR5 | CL38 | 5200 MT/s | 14.6ns |
| DDR5 | CL40 | 6000 MT/s | 13.3ns |
| DDR5 | CL32 | 6400 MT/s | 10ns |
GDDR: High-Bandwidth Memory for Parallel GPU Workloads
GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) is a memory architecture designed specifically for the high-bandwidth demands of modern GPUs. While it shares the SDRAM foundation with DDR system memory, GDDR is optimized for throughput, not latency. This makes it ideal for graphics rendering, massively parallel math operations, and data-heavy GPU compute tasks.
Unlike DDR, which prioritizes quick, low-latency access for CPUs, GPUs require extremely large amounts of data to be moved every second. GDDR achieves this by using wider buses, faster signaling, and higher sustained bandwidth, enabling GPUs to feed thousands of concurrent processing cores without stalling.
- Memory buses are significantly wider, ranging from 192-bit to as high as 512-bit buses on PCIe GPUs. The NVIDIA HGX feature HBM (a different type of GPU memory) has as high as a 8192-bit bus.
- Data transfer rates are much higher than DDR, enabling hundreds of GB/s to over 1 TB/s of bandwidth.
- The architecture is tuned for sequential, large-block data movement, matching the GPU’s linear and repetitive compute patterns.
This design ensures that pixel data, textures, model parameters, and compute workloads flow to the GPU cores without bottlenecking performance.
Unified Memory: The Bridge Between CPU and GPU
Unified Memory is not a new memory type like DDR or GDDR. Instead, it is a shared memory architecture and software abstraction that allows the CPU and GPU to operate on the same memory space without requiring the application to manually copy data back and forth.
Unified Memory removes this explicit memory transfer bottleneck, where data must be copied from system RAM (DDR/LPDDR) to GPU VRAM (GDDR/HBM) before the GPU can process it. Unified Memory presents CPU RAM and GPU VRAM as a single, unified address space. Under the hood:
- The memory is still physically separate (DDR for CPUs, GDDR/HBM for GPUs).
- Through hardware and driver support, both processors can access the same data.
Why Unified Memory Matters
Unified Memory offers benefits in both development and real-world performance:
- Simplified Programming: No manual memory copy calls; reduces bottlenecks
- Reduced Data Duplication: No separate host/device copies needed; ideal for AI/ML, simulations, analytics, and rendering
- Shared physical memory is a hardware architecture where CPU and GPU physically share the same memory pool (common in mobile devices and Apple’s M-series chips).
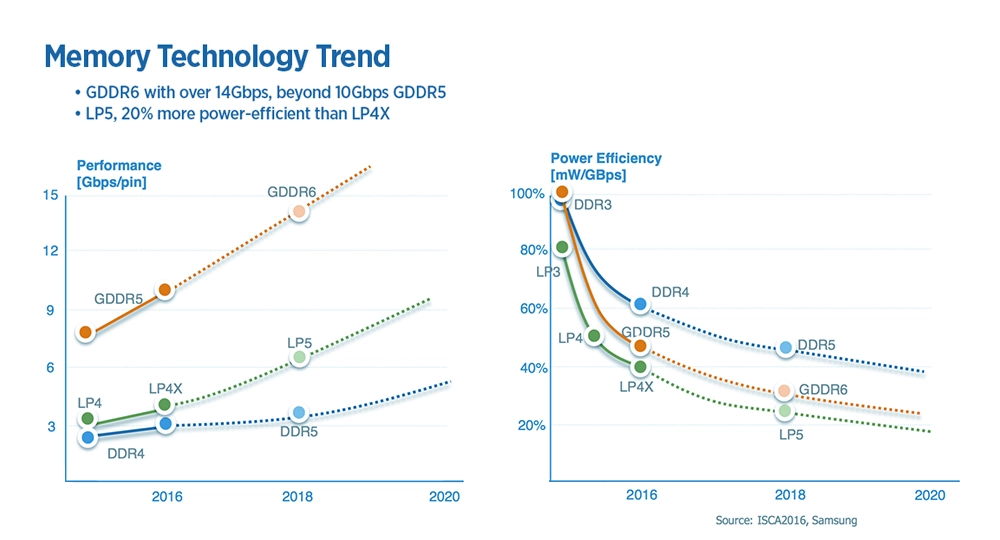
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
DDR memory provides the low-latency responsiveness that CPUs need for general-purpose computing, while GDDR delivers the massive bandwidth required to keep GPU cores fed with data during parallel processing tasks.
- DDR is optimized for latency: Designed to support CPU operations with quick, responsive access to diverse data patterns.
- GDDR is optimized for bandwidth: Built to handle the massive parallel data throughput demands of modern GPUs.
- Unified memory simplifies development: Eliminates manual data transfers between CPU and GPU memory spaces, improving efficiency in AI, simulation, and compute workloads.
- Each memory type serves a specific purpose: Understanding the strengths of DDR, GDDR, and unified memory helps you select the right hardware for your workload requirements.
- Memory architecture continues to evolve: With DDR5, GDDR7, and HBM advancing rapidly, staying informed about memory technology ensures you're leveraging the best tools for your applications.
Unified memory bridges CPU and GPU workflows by providing a shared address space, reducing manual data transfers, and streamlining workloads that have prolonged GPU and CPU memory saturation, such as AI and data analytics.
If you have questions about memory configurations, GPU workstations, or how to optimize your hardware for specific workloads, our team at Exxact Corporation is here to help. Whether you're designing a system for AI training, scientific computing, or high-performance rendering, we can guide you through selecting the right memory architecture and hardware components for your needs.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now
What's the Difference Between GDDR and DDR Memory?
What Does GDDR and DDR Stand For?
DDR stands for Double Data Rate, and GDDR stands for Graphics Double Data Rate. However, DDR and GDDR are completely different technologies—they don't share the same standards for speed, bandwidth, or other specifications. DDR is developed for CPUs (and CISC architectures), while GDDR is designed for graphics (and RISC architectures).
The full name GDDR7 SDRAM stands for Graphics Double Data Rate Type 7, Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory. Both DDR and GDDR use SDRAM—the foundation of memory used in desktops (UDIMM DDR5), in laptops (SODIMM DDR5), low-power devices (LPDDR5), and graphics processing units (GDDR6, GDDR6X, and GDDR7 in both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs).
Recent developments have introduced unified memory, a software abstraction that allows both CPU and GPU to share a memory pool. Popularized by Apple Macs, AMD APUs, and NVIDIA Grace, unified memory can use DDR or HBM memory. Unified memory is now used in the popular NVIDIA DGX Spark.
DDR: Low-Latency System Memory for General-Purpose Computing
DDR (Double Data Rate) memory is the primary system RAM used by CPUs. Unlike GDDR (optimized for bandwidth), DDR is designed for low latency, ensuring the CPU can access data and instructions as quickly and responsively as possible. This makes DDR ideal for running applications, managing the operating system, handling interrupts, and coordinating GPU workloads.
While CPU memory doesn’t reach the extreme transfer rates of GDDR or HBM, its strength lies in its ability to respond rapidly to a wide variety of small, random access patterns typical of general-purpose computing.
- Access times are optimized, measured in clock cycles (CAS Latency).
- Frequencies: DDR5 ranges from 4800 MT/s to beyond 8400 MT/s.
- Responsiveness over raw bandwidth: matches how CPUs process diverse, branching instruction sets.
These design choices ensure the CPU is never waiting long for data it needs to execute instructions, manage threads, or coordinate system resources.
Why DDR Matters
DDR provides several key benefits that directly affect everyday computing and workstation performance:
- Low Latency for CPU Operations: Essential for running applications, executing instructions, and managing real-time system tasks.
- High Efficiency for Random Access Patterns: Supports the CPU’s need to retrieve small chunks of data rapidly.
- Scalable Frequencies with Each Generation: DDR5 delivers higher transfer rates while improving efficiency and capacity.
- Latency vs. Frequency Balance: While DDR5 may have higher CAS Latency numbers than DDR4, its increased frequency results in similar or better absolute latency.
| DDR Generation | CAS Latency | Frequency | Absolute Latency |
| DDR4 | CL16 | 3200 MT/s | 10ns |
| DDR4 | CL18 | 3600 MT/s | 10ns |
| DDR5 | CL38 | 5200 MT/s | 14.6ns |
| DDR5 | CL40 | 6000 MT/s | 13.3ns |
| DDR5 | CL32 | 6400 MT/s | 10ns |
GDDR: High-Bandwidth Memory for Parallel GPU Workloads
GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) is a memory architecture designed specifically for the high-bandwidth demands of modern GPUs. While it shares the SDRAM foundation with DDR system memory, GDDR is optimized for throughput, not latency. This makes it ideal for graphics rendering, massively parallel math operations, and data-heavy GPU compute tasks.
Unlike DDR, which prioritizes quick, low-latency access for CPUs, GPUs require extremely large amounts of data to be moved every second. GDDR achieves this by using wider buses, faster signaling, and higher sustained bandwidth, enabling GPUs to feed thousands of concurrent processing cores without stalling.
- Memory buses are significantly wider, ranging from 192-bit to as high as 512-bit buses on PCIe GPUs. The NVIDIA HGX feature HBM (a different type of GPU memory) has as high as a 8192-bit bus.
- Data transfer rates are much higher than DDR, enabling hundreds of GB/s to over 1 TB/s of bandwidth.
- The architecture is tuned for sequential, large-block data movement, matching the GPU’s linear and repetitive compute patterns.
This design ensures that pixel data, textures, model parameters, and compute workloads flow to the GPU cores without bottlenecking performance.
Unified Memory: The Bridge Between CPU and GPU
Unified Memory is not a new memory type like DDR or GDDR. Instead, it is a shared memory architecture and software abstraction that allows the CPU and GPU to operate on the same memory space without requiring the application to manually copy data back and forth.
Unified Memory removes this explicit memory transfer bottleneck, where data must be copied from system RAM (DDR/LPDDR) to GPU VRAM (GDDR/HBM) before the GPU can process it. Unified Memory presents CPU RAM and GPU VRAM as a single, unified address space. Under the hood:
- The memory is still physically separate (DDR for CPUs, GDDR/HBM for GPUs).
- Through hardware and driver support, both processors can access the same data.
Why Unified Memory Matters
Unified Memory offers benefits in both development and real-world performance:
- Simplified Programming: No manual memory copy calls; reduces bottlenecks
- Reduced Data Duplication: No separate host/device copies needed; ideal for AI/ML, simulations, analytics, and rendering
- Shared physical memory is a hardware architecture where CPU and GPU physically share the same memory pool (common in mobile devices and Apple’s M-series chips).

Conclusion & Key Takeaways
DDR memory provides the low-latency responsiveness that CPUs need for general-purpose computing, while GDDR delivers the massive bandwidth required to keep GPU cores fed with data during parallel processing tasks.
- DDR is optimized for latency: Designed to support CPU operations with quick, responsive access to diverse data patterns.
- GDDR is optimized for bandwidth: Built to handle the massive parallel data throughput demands of modern GPUs.
- Unified memory simplifies development: Eliminates manual data transfers between CPU and GPU memory spaces, improving efficiency in AI, simulation, and compute workloads.
- Each memory type serves a specific purpose: Understanding the strengths of DDR, GDDR, and unified memory helps you select the right hardware for your workload requirements.
- Memory architecture continues to evolve: With DDR5, GDDR7, and HBM advancing rapidly, staying informed about memory technology ensures you're leveraging the best tools for your applications.
Unified memory bridges CPU and GPU workflows by providing a shared address space, reducing manual data transfers, and streamlining workloads that have prolonged GPU and CPU memory saturation, such as AI and data analytics.
If you have questions about memory configurations, GPU workstations, or how to optimize your hardware for specific workloads, our team at Exxact Corporation is here to help. Whether you're designing a system for AI training, scientific computing, or high-performance rendering, we can guide you through selecting the right memory architecture and hardware components for your needs.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now



.jpg?format=webp)