
Exxact Now Offers ARM Server Solutions powered by Ampere CPUs! Contact Us to inquire.
Why has ARM become more popular for HPC?
ARM CPUs have increasingly become more popular for HPC due to higher efficiency, density, scalability, and cloud nativity to manage IoT devices.
The data center and HPC industry have witnessed significant growth over the years, and with the explosion of big data, the demand for more efficient high-performance computing has become a huge endeavor. ARM processors, which are used in just about every smartphone on the planet, have become a viable option within the field of server solutions. For instance, the Fugaku in Japan, one of the world’s fastest supercomputers, runs on processors based on ARM architecture.
There has been an interest and shift from traditional x86 processors to ARM-based processors for certain workloads. ARM, which stands for Advanced RISC Machines, is a type of processor architecture that is widely used in mobile devices and is now gaining a foothold in data centers and HPC.
The data center and high-performance computing (HPC) spaces have long been dominated by x86 CPUs from AMD and Intel. However, Ampere's ARM CPUs are shaking up the industry and making waves in the data center and HPC industry by introducing various development platforms and cloud servers based on the ARM architecture. In this article, we'll dive deeper into ARM CPUs and the features that make them suitable for high-performance computing, and why they're such a game-changer.
What is ARM
ARM is a type of processor architecture that is widely used in mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets known for their low power consumption and efficient design first developed by Acorn in 1994. Nowadays, the chip design company Ampere holds a footing in the server ARM space.
One of the key differences between Ampere's ARM CPUs and traditional x86 CPUs is their architecture. ARM CPUs use a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, while x86 CPUs use a complex instruction set computing (CISC) architecture.
This means that ARM CPUs are able to perform computations more quickly and efficiently, as they require fewer instructions to carry out a given task. ARM CPUs are known for low power consumption, making them an attractive option for data centers and HPC to explore amidst the spike in energy consumption and cost.
ARM vs x86 CPUs

Performance per Watt
Power consumption is one of the critical factors in data centers and HPC. ARM processors consume less power compared to x86 processors, making them more power-efficient. With the increasing demand for power-efficient computing, ARM-based servers are becoming the go-to solution for data centers and HPC.
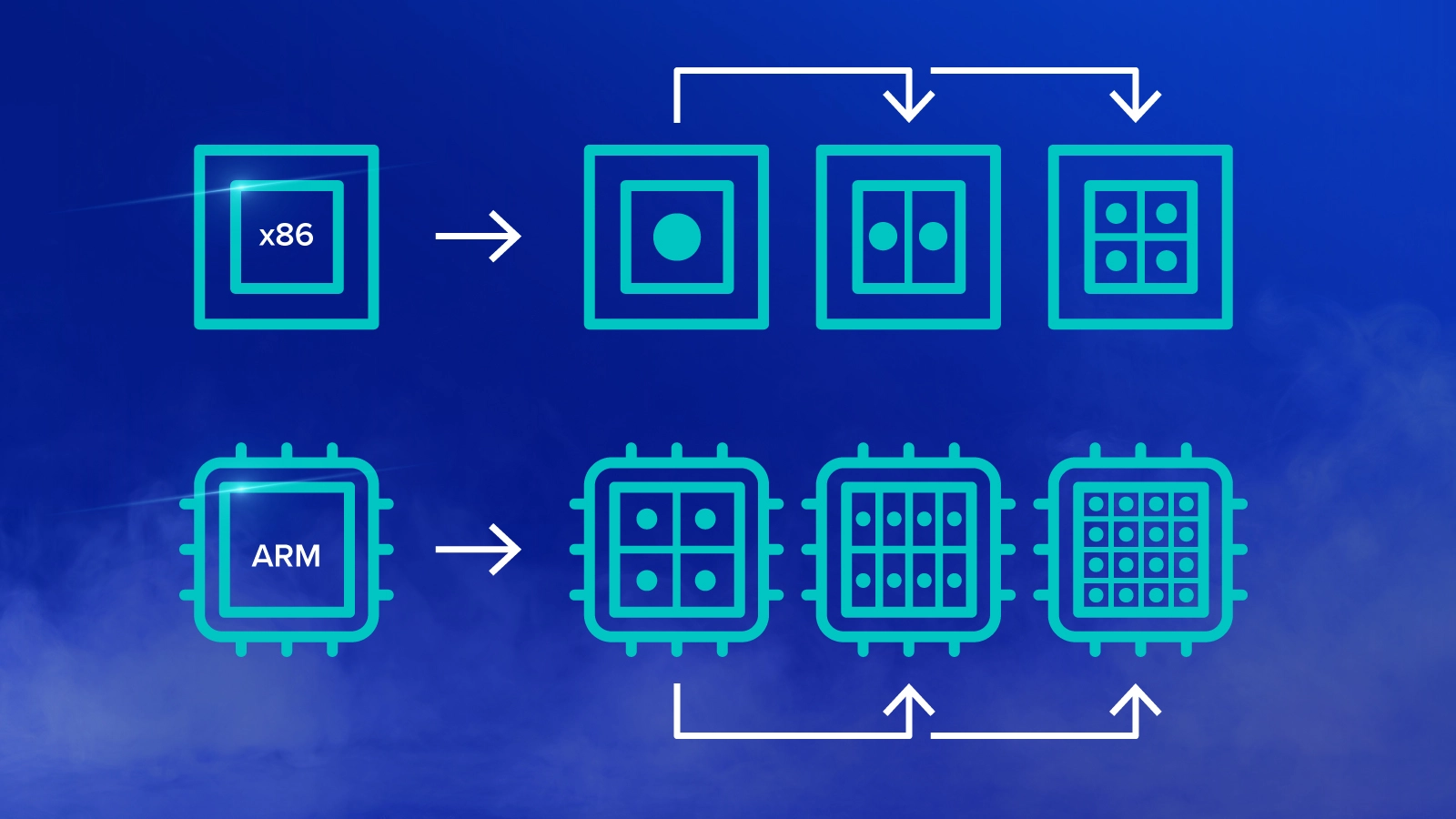
Workloads are distributed to a large amount of smaller, more efficient cores, instead of fewer more powerful cores. As a result, the cores of an ARM processor can offer better performance per watt of power on light workloads. Cloud-based applications that require around-the-clock operations such as web hosting, database management, and edge computing benefit from a low-power draw processor that can get the job done.
Better Thermals
Compared to x86 processors, ARM processors are known for their better energy efficiency due to their utilization of simple instructions that can be executed within a single clock cycle. The "reduced instructions" in RISC require fewer transistors and enable pipelining between different sets of instructions making ARM processors highly energy-efficient while minimizing heat generation, a crucial feature for mobile devices ARM processors. Remaining cool to prevent performance issues attributes prove beneficial for ARM server processors where efficient heat dissipation can boost performance and stability.
Cloud Native High-Density Computing
Ampere has placed its Altra and Altra Max processors in a position aimed toward hyper-scale cloud service providers, offering up to 128 cores. These providers are capable of developing software that scales efficiently with the number of cores instead of the performance of each core. This strategy limits the potential customer base for ARM-based solutions but as the data center grows and the popularity of the cloud increases, we can see an uplift in adoption.
Ampere currently places its Altra and Altra Max CPUs in the market at a lower price per core. By targeting the cloud computing space with its massive core counts and high efficiency to deliver the maximum amount of computing for the most amount of vCPUs (virtual-CPUs), Ampere is able to leverage a whole new market that runs their workloads at a lower power target for an even lower total cost.
Ampere Altra although new to the data center, can deliver x86 performance with the benefits of ARM. Invigorate your data center with Exxact Severs built with Ampere Altra and Altra Max.
Challenges with Adopting ARM
While ARM-based computer processors are being adopted by data centers, it is still a fairly young architecture that has yet to challenge the mainstream market that Intel and AMD hold. Ampere currently targets less complex applications and use cases. Databases, media encoding, web services, networking, cloud mobile gaming, and inferencing require their own individual processor and the density and power efficiency that ARM provides satisfies these light workloads.
To truly see further advancements of ARM for more complex acceleration in workloads such as Scientific Computing and training AI, we still need to look towards developers to support the ARM instruction set and the addition of accelerators like AVX-512. Its power efficiency can revolutionize high-performance computing to be handled cloud-natively.
One of the biggest challenges with adopting ARM-based processors is software compatibility. Most applications are designed to run on x86 processors, which means they need to be recompiled to run on ARM processors. This can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for companies that have a large number of applications.
The Future of ARM
Many modern handheld technologies are powered by ARM processors. Its energy efficiency to power some of the most complex smartphone tasks to date showcases its potential to drive data center workloads. We can see Apple’s ARM-based M1 and M2 chips have little performance competition in the consumer laptop market. IoT devices like autonomous vehicles and robots are all built on RISC and ARM.
The move towards higher efficiency and lower power for those lighter data centers and cloud-based tasks can reserve the raw computing that x86 servers have for more complex and heavy-duty workloads. Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google have turned towards using ARM-based processors in their cloud-native computing.
As cloud providers look to increase the energy efficiency of their data centers, ARM processors are likely to become an increasingly popular choice for powering cloud instances. Startups can leverage the lower cost to run these systems for new and exciting innovations in the connected world.
Exxact is now offering ARM Servers powered by Ampere Altra and Altra Max!
Contact Us today for more info.

Why ARM is Becoming More Popular in Data Centers and HPC
Exxact Now Offers ARM Server Solutions powered by Ampere CPUs! Contact Us to inquire.
Why has ARM become more popular for HPC?
ARM CPUs have increasingly become more popular for HPC due to higher efficiency, density, scalability, and cloud nativity to manage IoT devices.
The data center and HPC industry have witnessed significant growth over the years, and with the explosion of big data, the demand for more efficient high-performance computing has become a huge endeavor. ARM processors, which are used in just about every smartphone on the planet, have become a viable option within the field of server solutions. For instance, the Fugaku in Japan, one of the world’s fastest supercomputers, runs on processors based on ARM architecture.
There has been an interest and shift from traditional x86 processors to ARM-based processors for certain workloads. ARM, which stands for Advanced RISC Machines, is a type of processor architecture that is widely used in mobile devices and is now gaining a foothold in data centers and HPC.
The data center and high-performance computing (HPC) spaces have long been dominated by x86 CPUs from AMD and Intel. However, Ampere's ARM CPUs are shaking up the industry and making waves in the data center and HPC industry by introducing various development platforms and cloud servers based on the ARM architecture. In this article, we'll dive deeper into ARM CPUs and the features that make them suitable for high-performance computing, and why they're such a game-changer.
What is ARM
ARM is a type of processor architecture that is widely used in mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets known for their low power consumption and efficient design first developed by Acorn in 1994. Nowadays, the chip design company Ampere holds a footing in the server ARM space.
One of the key differences between Ampere's ARM CPUs and traditional x86 CPUs is their architecture. ARM CPUs use a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, while x86 CPUs use a complex instruction set computing (CISC) architecture.
This means that ARM CPUs are able to perform computations more quickly and efficiently, as they require fewer instructions to carry out a given task. ARM CPUs are known for low power consumption, making them an attractive option for data centers and HPC to explore amidst the spike in energy consumption and cost.
ARM vs x86 CPUs

Performance per Watt
Power consumption is one of the critical factors in data centers and HPC. ARM processors consume less power compared to x86 processors, making them more power-efficient. With the increasing demand for power-efficient computing, ARM-based servers are becoming the go-to solution for data centers and HPC.
Workloads are distributed to a large amount of smaller, more efficient cores, instead of fewer more powerful cores. As a result, the cores of an ARM processor can offer better performance per watt of power on light workloads. Cloud-based applications that require around-the-clock operations such as web hosting, database management, and edge computing benefit from a low-power draw processor that can get the job done.
Better Thermals
Compared to x86 processors, ARM processors are known for their better energy efficiency due to their utilization of simple instructions that can be executed within a single clock cycle. The "reduced instructions" in RISC require fewer transistors and enable pipelining between different sets of instructions making ARM processors highly energy-efficient while minimizing heat generation, a crucial feature for mobile devices ARM processors. Remaining cool to prevent performance issues attributes prove beneficial for ARM server processors where efficient heat dissipation can boost performance and stability.
Cloud Native High-Density Computing
Ampere has placed its Altra and Altra Max processors in a position aimed toward hyper-scale cloud service providers, offering up to 128 cores. These providers are capable of developing software that scales efficiently with the number of cores instead of the performance of each core. This strategy limits the potential customer base for ARM-based solutions but as the data center grows and the popularity of the cloud increases, we can see an uplift in adoption.
Ampere currently places its Altra and Altra Max CPUs in the market at a lower price per core. By targeting the cloud computing space with its massive core counts and high efficiency to deliver the maximum amount of computing for the most amount of vCPUs (virtual-CPUs), Ampere is able to leverage a whole new market that runs their workloads at a lower power target for an even lower total cost.
Ampere Altra although new to the data center, can deliver x86 performance with the benefits of ARM. Invigorate your data center with Exxact Severs built with Ampere Altra and Altra Max.

Challenges with Adopting ARM
While ARM-based computer processors are being adopted by data centers, it is still a fairly young architecture that has yet to challenge the mainstream market that Intel and AMD hold. Ampere currently targets less complex applications and use cases. Databases, media encoding, web services, networking, cloud mobile gaming, and inferencing require their own individual processor and the density and power efficiency that ARM provides satisfies these light workloads.
To truly see further advancements of ARM for more complex acceleration in workloads such as Scientific Computing and training AI, we still need to look towards developers to support the ARM instruction set and the addition of accelerators like AVX-512. Its power efficiency can revolutionize high-performance computing to be handled cloud-natively.
One of the biggest challenges with adopting ARM-based processors is software compatibility. Most applications are designed to run on x86 processors, which means they need to be recompiled to run on ARM processors. This can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for companies that have a large number of applications.
The Future of ARM
Many modern handheld technologies are powered by ARM processors. Its energy efficiency to power some of the most complex smartphone tasks to date showcases its potential to drive data center workloads. We can see Apple’s ARM-based M1 and M2 chips have little performance competition in the consumer laptop market. IoT devices like autonomous vehicles and robots are all built on RISC and ARM.
The move towards higher efficiency and lower power for those lighter data centers and cloud-based tasks can reserve the raw computing that x86 servers have for more complex and heavy-duty workloads. Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google have turned towards using ARM-based processors in their cloud-native computing.
As cloud providers look to increase the energy efficiency of their data centers, ARM processors are likely to become an increasingly popular choice for powering cloud instances. Startups can leverage the lower cost to run these systems for new and exciting innovations in the connected world.
Exxact is now offering ARM Servers powered by Ampere Altra and Altra Max!
Contact Us today for more info.

