Introduction to Ansys Rocky Licensing
With an extensive library, Ansys has an equally complex licensing format. Enabling more compute nodes or higher-performance hardware would require additional licenses. Previously, we explored the main licensing formal formats for HPC Packs for Ansys Mechanical, Fluent, HFSS, and more.
We will go over Ansys Rocky licensing in this blog called HPC Tasks and HPC Features which use a GPU’s SMs as the variable in determining the number of licenses needed to enable full use of your system configuration.
Before we get into the nitty gritty detail of calculating the Ansys Rocky Licensing Model, we first need to define SMs.
What are SMs or Streaming Multiprocessors?
Streaming multiprocessors are the architectural parallel processing units that make up an entire GPU. An SM will contain multiple CUDA cores as well as the shared memory cache, schedulers, and registers. Think of GPU SMs as groups of workers tasked with computations, memory management, and instruction pipelines.
Finding the SMs count of a GPU is not as simple as looking at the specifications table on NVIDIA’s website. In the examples used, we list popular GPU configurations and their SM count. You can also find the SM count of a GPU on Techpowerup's GPU Database.
An SM is the GPU equivalent to a CPU core, hence why many Ansys licensing models refer to a GPU’s SMs as the variable for their licensing tiers.
Ansys Rocky Licensing - HPC Tasks & HPC Features
Ansys HPC Tasks are the licenses that define the total supported SMs or streaming multiprocessors in your GPU configuration enabled for your Ansys Rocky calculation. It is important to note that Ansys Rocky allows you to run on a GPU without requiring a single license supporting up to 112 SMs.
When you choose to utilize a GPU with greater than 112 SMs, you are then required to purchase a Rocky HPC Task Licenses and subsequent HPC Features to enable past 112 SMs. Therefore if we are running a GPU with hypothetically 113 SMs, we are required to purchase 1 Task + 1 Feature to cover 112 + 14 SMs.
- 1 HPC Task = 8 HPC Features = 112 SMs allowed, therefore
- 1 HPC Feature = 14 SMs enabled
| Rocky HPC Tasks | SMs Supported |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 - 112 |
| 1 | 112 - 224 |
| 2 | 224 - 336 |
| 3 | 336 - 448 |
| 4 | 448 - 560 |
Use this table to determine the number of HPC Tasks licenses needed by evaluating the total SMs in your hardware configuration. More on how to find To determine the number of HPC Features needed, the formula is as follows:
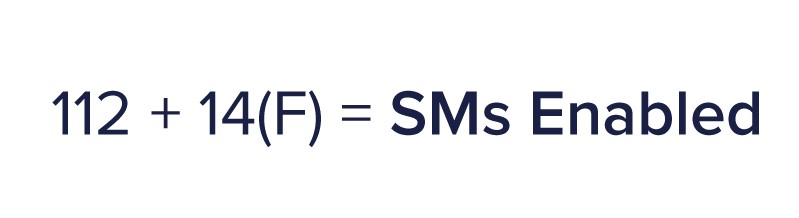
When using the formula above, SMs Enabled must exceed the number of SMs in your hardware configuration, thus Features variable F will be rounded up to the next whole number. Therefore, to calculate the number of Features required, we substitute SMs Enabled with SMs in Configuration. You cannot purchase half or a quarter of a Feature so in our formula we round to the next whole number denoted by ‘ceiling’ in mathematical terminology (which looks like a bracket without feet).

Let’s use an example: If your configuration has 400 SMs. First and foremost, since 400 SMs falls between 336 and 448, 3 HPC Tasks are required. We then run our formula for determining the number of HPC Features needed:

Calculating Rocky License with GPUs
Finding a GPU’s SM count is not as straightforward as looking at the product specifications. Listed are the current generation professional RTX GPUs and data center GPUs that accelerate Ansys Rocky along with its licensing requirements.
| GPU | SM Count | HPC Tasks | Features | GPU Memory | Designation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTX 2000 Ada | 22 | - | - | 16GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 4000 Ada | 48 | - | - | 20GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 4500 Ada | 60 | - | - | 24GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 5000 Ada | 100 | - | - | 32GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 6000 Ada | 142 | 1 Task | 3 Features | 48GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| NVIDIA A800 40GB Active | 108 | - | - | 40GB HBM2e | Workstation |
| NVIDIA A100 | 108 | - | - | 80GB HBM2e | Server |
| NVIDIA H100 | 114 | 1 Task | 1 Features | 80GB HBM2e | Server |
| NVIDIA H100 NVL | 132 | 1 Task | 2 Features | 96GB HBM3 | Server |
If the GPU configuration exceeds the SM count threshold for a Rocky HPC Task license, you are required to purchase an HPC Task with its subsequent HPC Features to make up the difference.
For example, if we have a system with dual RTX 4500 Ada (48SMs each totaling 96SMs) we would not be required to purchase an HPC Tasks. However, for running 3 RTX 4500 Ada (48SMs each totaling 144SMs) we would be required to purchase 1 HPC Tasks (112SMs) + 3 HPC Features (14SMs each totaling 42SMs) = 154SMs enabled.
Let’s examine common configurations from our customers and their Rocky Licensing outlook:
| GPU | SM Count | HPC Tasks | HPC Features | GPU Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1x RTX 4500 Ada | 48 | - | - | 24GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 4500 Ada | 96 | - | - | 48GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 4500 Ada | 192 | 1 Task | 6 Features | 96GB GDDR6 |
| 1x RTX 5000 Ada | 100 | - | - | 32GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 5000 Ada | 200 | 1 Task | 7 Features | 64GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 5000 Ada | 400 | 3 Tasks | 21 Features | 128GB GDDR6 |
| 1x RTX 6000 Ada | 142 | 1 Task | 3 Features | 48GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 6000 Ada | 284 | 2 Tasks | 13 Features | 96GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 6000 Ada | 568 | 5 Tasks | 33 Features | 192GB GDDR6 |
| 1x NVIDIA H100 | 114 | 1 Task | 1 Feature | 80GB HBM2e |
| 2x NVIDIA H100 | 228 | 2 Tasks | 9 Features | 160GB HBM2e |
| 4x NVIDIA H100 | 456 | 4 Tasks | 25 Features | 320GB HBM2e |
| 1x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 132 | 1 Task | 2 Features | 96GB HBM3 |
| 2x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 264 | 2 Tasks | 11 Features | 192GB HBM3 |
| 4x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 528 | 4 Tasks | 30 Features | 384GB HBM3 |
Ansys Rocky GPU Considerations
Ansys Rocky performance increases with memory size and bandwidth. The higher the memory size, the larger the model can fit on a single GPU and the larger memory bandwidth increases the performance in the processing pipeline.
Performance is also dictated by the type of DEM models you run; spherical, non-spherical shaped, and SPH elements.
| Spherical Particles Only | Non-Spherical & SPH |
|---|---|
| Can be executed on FP32 or single precision. Prioritize high memory bandwidth and large GPU memory. You can run small model sizes of non-spherical and SPH models with these GPUs. All professional RTX GPUs have video output and are perfect for engineering workstations. | Requires FP64 or double-precision native GPUs. These enterprise GPUs with FP64 native come with high memory bandwidth and GPU memory offering the best performance and flexibility at a higher cost but have no video output. You will need a dedicated display card to use a server as a compute-only system. |
| NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada NVIDIA RTX 5000 Ada NVIDIA RTX 4500 Ada NVIDIA A800 40GB Active | NVIDIA A100 80GB PCIe NVIDIA A800 40GB Active NVIDIA H100 80GB PCIe NVIDIA H100 NVL 96GB PCIe |
Ansys Rocky supports multi-GPU configurations for increasing GPU memory size for larger models as well as increased performance for even faster results. With a single H100 running either a spherical or non-spherical model, we expect over 10x faster results. Faster results mean your operation can run an increased number of iterations to finetune your machinery, product, or factory.
Conclusions
Accelerating computations in Ansys is paramount for engineers in perfecting their machinery or product design. Running simulations have reduced the cost already and accelerating those simulations not only decreases risk but increases predictability and identifying faults.
Optimizing price to performance is essential for maximizing value when investing in high-performance computing and GPU-accelerated computing. Exxact is here to deliver the right system and tools for enabling reduced simulation time and success. If you have any questions regarding hardware configurations, contact our team and we will help guide you in the right direction.

Accelerate Simulations in Ansys with GPUs
With the latest CPUs and most powerful GPUs available, accelerate your Ansys simulation and CFD project optimized to your deployment, budget, and desired performance!
Configure Now
Ansys Rocky Licensing for CPUs & GPUs Explained
Introduction to Ansys Rocky Licensing
With an extensive library, Ansys has an equally complex licensing format. Enabling more compute nodes or higher-performance hardware would require additional licenses. Previously, we explored the main licensing formal formats for HPC Packs for Ansys Mechanical, Fluent, HFSS, and more.
We will go over Ansys Rocky licensing in this blog called HPC Tasks and HPC Features which use a GPU’s SMs as the variable in determining the number of licenses needed to enable full use of your system configuration.
Before we get into the nitty gritty detail of calculating the Ansys Rocky Licensing Model, we first need to define SMs.
What are SMs or Streaming Multiprocessors?
Streaming multiprocessors are the architectural parallel processing units that make up an entire GPU. An SM will contain multiple CUDA cores as well as the shared memory cache, schedulers, and registers. Think of GPU SMs as groups of workers tasked with computations, memory management, and instruction pipelines.
Finding the SMs count of a GPU is not as simple as looking at the specifications table on NVIDIA’s website. In the examples used, we list popular GPU configurations and their SM count. You can also find the SM count of a GPU on Techpowerup's GPU Database.
An SM is the GPU equivalent to a CPU core, hence why many Ansys licensing models refer to a GPU’s SMs as the variable for their licensing tiers.
Ansys Rocky Licensing - HPC Tasks & HPC Features
Ansys HPC Tasks are the licenses that define the total supported SMs or streaming multiprocessors in your GPU configuration enabled for your Ansys Rocky calculation. It is important to note that Ansys Rocky allows you to run on a GPU without requiring a single license supporting up to 112 SMs.
When you choose to utilize a GPU with greater than 112 SMs, you are then required to purchase a Rocky HPC Task Licenses and subsequent HPC Features to enable past 112 SMs. Therefore if we are running a GPU with hypothetically 113 SMs, we are required to purchase 1 Task + 1 Feature to cover 112 + 14 SMs.
- 1 HPC Task = 8 HPC Features = 112 SMs allowed, therefore
- 1 HPC Feature = 14 SMs enabled
| Rocky HPC Tasks | SMs Supported |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 - 112 |
| 1 | 112 - 224 |
| 2 | 224 - 336 |
| 3 | 336 - 448 |
| 4 | 448 - 560 |
Use this table to determine the number of HPC Tasks licenses needed by evaluating the total SMs in your hardware configuration. More on how to find To determine the number of HPC Features needed, the formula is as follows:
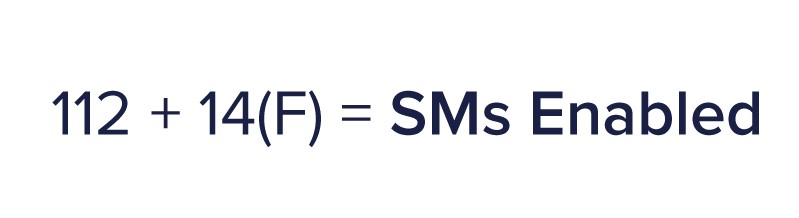
When using the formula above, SMs Enabled must exceed the number of SMs in your hardware configuration, thus Features variable F will be rounded up to the next whole number. Therefore, to calculate the number of Features required, we substitute SMs Enabled with SMs in Configuration. You cannot purchase half or a quarter of a Feature so in our formula we round to the next whole number denoted by ‘ceiling’ in mathematical terminology (which looks like a bracket without feet).

Let’s use an example: If your configuration has 400 SMs. First and foremost, since 400 SMs falls between 336 and 448, 3 HPC Tasks are required. We then run our formula for determining the number of HPC Features needed:

Calculating Rocky License with GPUs
Finding a GPU’s SM count is not as straightforward as looking at the product specifications. Listed are the current generation professional RTX GPUs and data center GPUs that accelerate Ansys Rocky along with its licensing requirements.
| GPU | SM Count | HPC Tasks | Features | GPU Memory | Designation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTX 2000 Ada | 22 | - | - | 16GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 4000 Ada | 48 | - | - | 20GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 4500 Ada | 60 | - | - | 24GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 5000 Ada | 100 | - | - | 32GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| RTX 6000 Ada | 142 | 1 Task | 3 Features | 48GB GDDR6 | Workstation |
| NVIDIA A800 40GB Active | 108 | - | - | 40GB HBM2e | Workstation |
| NVIDIA A100 | 108 | - | - | 80GB HBM2e | Server |
| NVIDIA H100 | 114 | 1 Task | 1 Features | 80GB HBM2e | Server |
| NVIDIA H100 NVL | 132 | 1 Task | 2 Features | 96GB HBM3 | Server |
If the GPU configuration exceeds the SM count threshold for a Rocky HPC Task license, you are required to purchase an HPC Task with its subsequent HPC Features to make up the difference.
For example, if we have a system with dual RTX 4500 Ada (48SMs each totaling 96SMs) we would not be required to purchase an HPC Tasks. However, for running 3 RTX 4500 Ada (48SMs each totaling 144SMs) we would be required to purchase 1 HPC Tasks (112SMs) + 3 HPC Features (14SMs each totaling 42SMs) = 154SMs enabled.
Let’s examine common configurations from our customers and their Rocky Licensing outlook:
| GPU | SM Count | HPC Tasks | HPC Features | GPU Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1x RTX 4500 Ada | 48 | - | - | 24GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 4500 Ada | 96 | - | - | 48GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 4500 Ada | 192 | 1 Task | 6 Features | 96GB GDDR6 |
| 1x RTX 5000 Ada | 100 | - | - | 32GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 5000 Ada | 200 | 1 Task | 7 Features | 64GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 5000 Ada | 400 | 3 Tasks | 21 Features | 128GB GDDR6 |
| 1x RTX 6000 Ada | 142 | 1 Task | 3 Features | 48GB GDDR6 |
| 2x RTX 6000 Ada | 284 | 2 Tasks | 13 Features | 96GB GDDR6 |
| 4x RTX 6000 Ada | 568 | 5 Tasks | 33 Features | 192GB GDDR6 |
| 1x NVIDIA H100 | 114 | 1 Task | 1 Feature | 80GB HBM2e |
| 2x NVIDIA H100 | 228 | 2 Tasks | 9 Features | 160GB HBM2e |
| 4x NVIDIA H100 | 456 | 4 Tasks | 25 Features | 320GB HBM2e |
| 1x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 132 | 1 Task | 2 Features | 96GB HBM3 |
| 2x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 264 | 2 Tasks | 11 Features | 192GB HBM3 |
| 4x NVIDIA H100 NVL | 528 | 4 Tasks | 30 Features | 384GB HBM3 |
Ansys Rocky GPU Considerations
Ansys Rocky performance increases with memory size and bandwidth. The higher the memory size, the larger the model can fit on a single GPU and the larger memory bandwidth increases the performance in the processing pipeline.
Performance is also dictated by the type of DEM models you run; spherical, non-spherical shaped, and SPH elements.
| Spherical Particles Only | Non-Spherical & SPH |
|---|---|
| Can be executed on FP32 or single precision. Prioritize high memory bandwidth and large GPU memory. You can run small model sizes of non-spherical and SPH models with these GPUs. All professional RTX GPUs have video output and are perfect for engineering workstations. | Requires FP64 or double-precision native GPUs. These enterprise GPUs with FP64 native come with high memory bandwidth and GPU memory offering the best performance and flexibility at a higher cost but have no video output. You will need a dedicated display card to use a server as a compute-only system. |
| NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada NVIDIA RTX 5000 Ada NVIDIA RTX 4500 Ada NVIDIA A800 40GB Active | NVIDIA A100 80GB PCIe NVIDIA A800 40GB Active NVIDIA H100 80GB PCIe NVIDIA H100 NVL 96GB PCIe |
Ansys Rocky supports multi-GPU configurations for increasing GPU memory size for larger models as well as increased performance for even faster results. With a single H100 running either a spherical or non-spherical model, we expect over 10x faster results. Faster results mean your operation can run an increased number of iterations to finetune your machinery, product, or factory.
Conclusions
Accelerating computations in Ansys is paramount for engineers in perfecting their machinery or product design. Running simulations have reduced the cost already and accelerating those simulations not only decreases risk but increases predictability and identifying faults.
Optimizing price to performance is essential for maximizing value when investing in high-performance computing and GPU-accelerated computing. Exxact is here to deliver the right system and tools for enabling reduced simulation time and success. If you have any questions regarding hardware configurations, contact our team and we will help guide you in the right direction.

Accelerate Simulations in Ansys with GPUs
With the latest CPUs and most powerful GPUs available, accelerate your Ansys simulation and CFD project optimized to your deployment, budget, and desired performance!
Configure Now